What Is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a digital currency that operates on a decentralized network of computers, called nodes, which communicate with each other to validate transactions and keep the ledger up-to-date. The Bitcoin network uses a distributed ledger technology called blockchain to record and secure all transactions. Bitcoin was created in 2009 by an unknown person or group of people using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. It is commonly referred to as a “cryptocurrency,” as it uses public-key cryptography to secure and verify transactions.
Unlike traditional currency that can be printed by governments, there will only ever be 21 million Bitcoins in existence. This makes it similar to gold and other valuable resources, which also have a limited supply.

Bitcoin transactions are irreversible, meaning that once a transaction is made, it cannot be undone. This is because once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it is there permanently. This feature makes BTC transactions highly secure and difficult to hack or fraud.
Bitcoin has been gaining popularity as a store of value and method of payment in recent years, but it is still considered to be a highly speculative investment. Its value has been known to be highly volatile, and it is not yet widely accepted as a form of payment by mainstream merchants and businesses. Despite this, many individuals and institutions have begun to invest in BTC, and it is thought by some to have the potential to become a major player in the global financial system.
How Bitcoin works
Bitcoin works using a decentralized system of technology, when a transaction is made using BTC, the details of the transaction, such as the amount and the addresses of the sender and receiver, are grouped together in a “block.” This block is then broadcast to the entire network of computers that make up the Bitcoin network. These computers, called “nodes,” then work to validate the transaction by solving complex mathematical equations.
Once a block of transactions is validated, it is added to the existing chain of blocks, known as the blockchain. The blockchain is maintained by a decentralized group of individuals and organizations known as “miners.” Miners use powerful computers to validate transactions and are rewarded with newly created bitcoins for their efforts.
Let’s say you want to send some BTC to your friend who lives in another country. Here’s how the process would work:
- You would first need to have a digital wallet that stores your BTC. You can think of a digital wallet as a virtual bank account for BTC.
- You would need to get your friend’s BTC address. This is a unique code, like a long string of numbers and letters, that identifies your friend’s BTC wallet.
- Once you have your friend’s BTC address, you can enter it into your own digital wallet and enter the amount of BTC you want to send.
- Your wallet then broadcasts the transaction to the Bitcoin network, which is made up of a large number of computers (nodes) that are connected to each other.
- These nodes work together to validate your transaction, making sure that you have enough BTC in your account to send to your friend, and that you’re not trying to send the same BTC to multiple people at once.
- Once your transaction is validated by the network, it’s added to the blockchain. The blockchain is a public ledger that records every Bitcoin transaction ever made.
- The BTC you sent is now deducted from your wallet, and added to your friend’s wallet. The entire process is usually completed within a few minutes.

How to Mine Bitcoin?
Mining Bitcoin involves using specialized computer hardware to validate transactions on the Bitcoin network and to add them to the blockchain. By doing so, miners are rewarded with newly created bitcoins. Here are the basic steps involved in mining BTC:
- Obtain the necessary hardware: In order to mine BTC, you will need specialized computer hardware, known as an ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) miner. These miners are specifically designed for the purpose of mining Bitcoin and are much more powerful than a standard computer.
- Join a mining pool: Mining Bitcoin on your own can be difficult and unprofitable, so many miners choose to join a mining pool. A mining pool is a group of miners who combine their computing power to increase their chances of finding a block and earning rewards.
- Download mining software: Once you have your hardware and have joined a mining pool, you will need to download mining software to control your miner and connect it to the pool.
- Set up the miner: Once the software is installed, you will need to set up your miner by configuring it to connect to the mining pool and to your Bitcoin wallet.
- Start mining: Once your miner is set up, you can start the process of mining BTC. This involves using the computing power of your miner to validate transactions on the Bitcoin network and to add them to the blockchain.
- Earn rewards: As you validate transactions, you will earn rewards in the form of newly created bitcoins. These rewards are typically shared among all the members of the mining pool.
It’s worth noting that mining BTC is a highly competitive process and the difficulty to mine is high, the energy consumption is also high and the reward for mining a block is not as high as it used to be, so it’s not as profitable as it used to be. Moreover, with the increasing difficulty of mining process, smaller miners may find it hard to compete with larger miners and end up losing money.
How to get Bitcoin(BTC)
There are several ways to acquire Bitcoin, including:
- Buying Bitcoin on a cryptocurrency exchange: One of the most common ways to acquire BTC is to buy it on a cryptocurrency exchange. These are online platforms that allow you to buy and sell Bitcoin, as well as other cryptocurrencies, using fiat currency or other cryptocurrencies. Some popular exchanges include Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken.
- Accepting Bitcoin as payment: If you provide goods or services, you can accept Bitcoin as payment. This can be done by setting up a digital wallet and providing your customers with your Bitcoin address.
- Mining Bitcoin: Bitcoin can be acquired through a process called mining, which involves using specialized computer hardware to validate transactions on the Bitcoin network and to add them to the blockchain. Miners are rewarded with newly created bitcoins for their efforts.
- Bitcoin ATMs: Bitcoin ATMs are a physical machine that enables you to buy or sell bitcoins for cash.
- Bitcoin faucets: They are websites that give away small amounts of bitcoin in exchange for completing simple tasks or captchas.
- Bitcoin giveaways and airdrops: Some companies and projects occasionally give away or airdrop free bitcoins to their community or holders of their tokens.
It’s important to note that buying BTC or any other cryptocurrency, may be considered as a high-risk investment and it’s highly volatile. It is recommended to do your own research and understand the risks before investing.
How to use Bitcoin
Once you have acquired some Bitcoin, here are a few ways to use it:
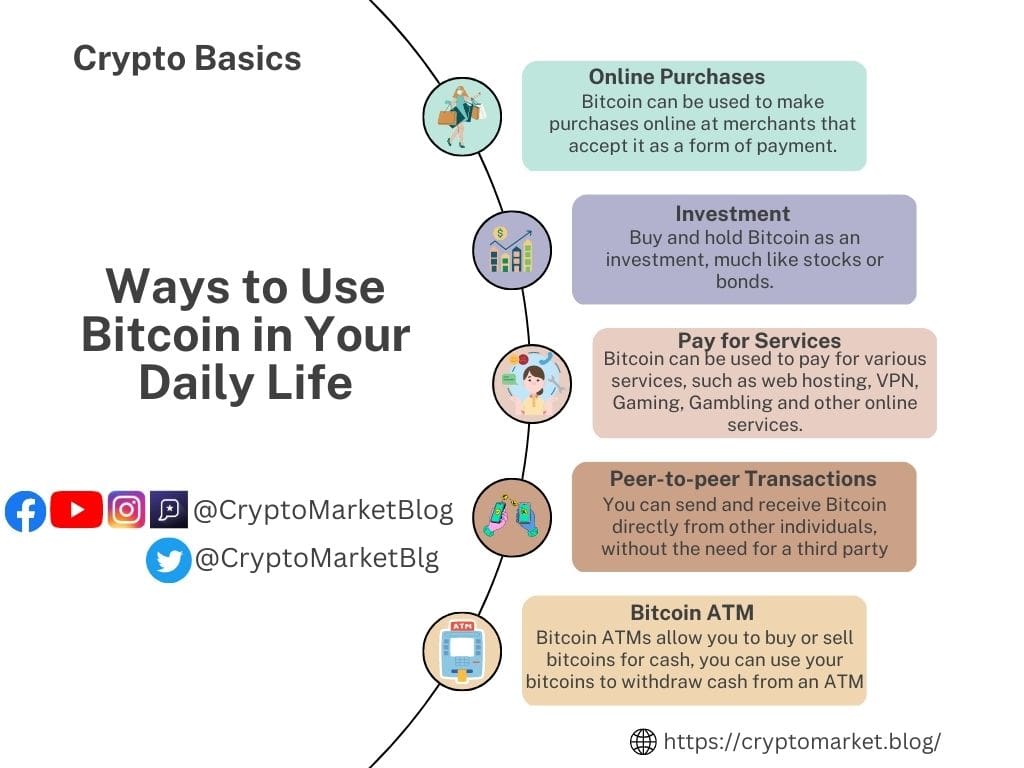
- Online Purchases: BTC can be used to make purchases online at merchants that accept it as a form of payment. These include a growing number of online retailers, as well as some brick-and-mortar businesses.
- Transactions with other individuals: Bitcoin can be used to send money to other individuals, just like sending an email. All you need is the recipient’s Bitcoin address.
- Investing: Some people purchase Bitcoin as a form of investment, with the expectation that its value will increase over time.
- Using Bitcoin ATM: Bitcoin ATMs allow you to buy or sell bitcoins for cash, you can use your bitcoins to withdraw cash from an ATM.
- Pay for services: BTC can be used to pay for various services, such as web hosting, VPN, and other online services.
- Gambling: Some online casinos and gambling sites accept BTCas a form of payment.
It’s important to keep in mind that the use of Bitcoin is still relatively limited compared to traditional fiat currencies and its acceptance is not yet as widespread. Additionally, the value of BTC is highly volatile, so it’s important to be aware of the risks before using it for transactions.
What makes Bitcoin a new kind of money?
Bitcoin is often referred to as a new kind of money because it operates differently from traditional fiat currencies. Some of the key differences include:
- Decentralization: Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network, meaning that it is not controlled by any government or institution. Instead, it relies on a network of computers that work together to process and record transactions.
- Limited Supply: BTC has a finite supply of 21 million, which cannot be increased. This is different from traditional fiat currencies, which can be printed by governments.
- Transparency: BTC transactions are recorded on a public digital ledger called the blockchain, which provides a transparent and tamper-proof record of all transactions.
- Anonymity: While transactions are recorded on the blockchain, the identities of the parties involved in the transaction are not revealed.
- Security: BTC transactions are secured by complex cryptography, making them resistant to fraud and hacking.
- Borderless: Bitcoin is borderless, meaning that it can be used anywhere in the world, as long as there is an internet connection and a device to access it.
- Censorship-Resistant: BTC is censorship-resistant, meaning that no one can prevent transactions from happening or prevent access to the Bitcoin network.
- Independence from government: Bitcoin operates outside of government and central bank control, giving users more control over their own funds and financial privacy.
- Immutability: Once confirmed, a BTC transaction cannot be altered or reversed, providing a level of security and transparency not possible with traditional banking systems.
- Store of Value: Many people view BTC as a digital store of value, similar to gold or other precious metals, which can be held as a long-term investment or used as a hedge against economic instability.
- Low Transaction Fees: BTC transactions typically have lower fees than traditional financial transactions, making it more accessible to people who would otherwise be excluded from the financial system.
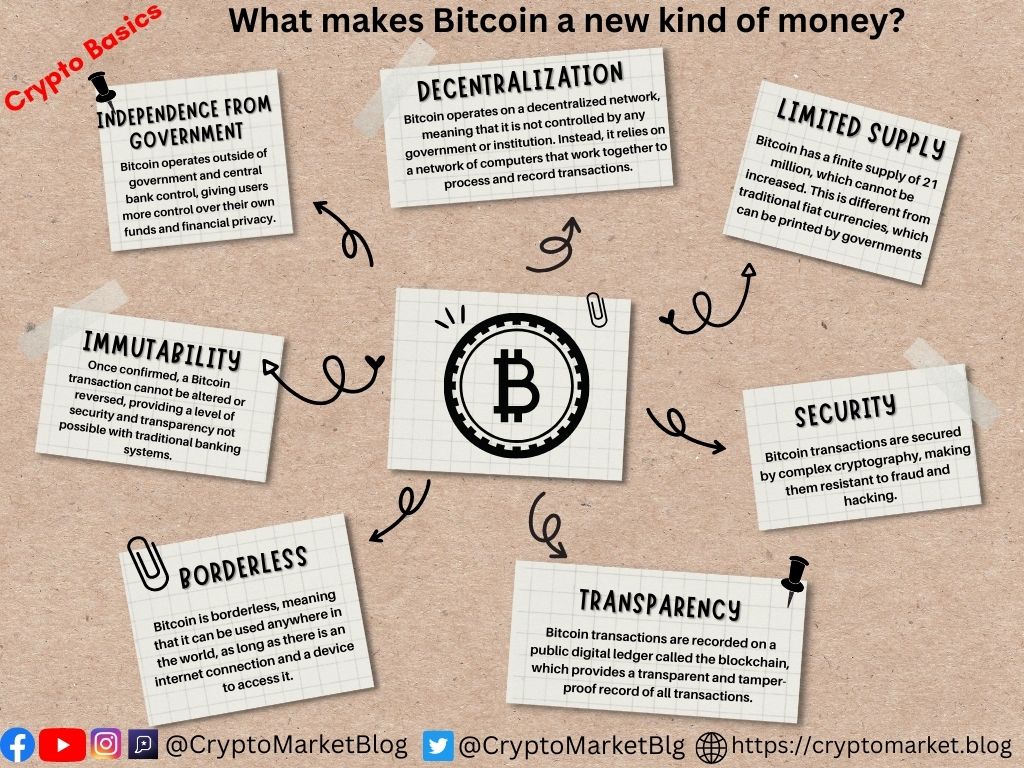
These features make Bitcoin a new kind of money that is not controlled by any central authority and offers a high degree of transparency, security, and autonomy to its users.
What are the problems with bitcoin?
Bitcoin, like any other technology, has its own set of problems and challenges. Some of the key issues include:
- Scalability: As the number of transactions on the Bitcoin network increases, it has become increasingly difficult for the network to process all the transactions quickly and efficiently. This has led to delays and higher transaction fees.
- Energy consumption: Bitcoin mining requires a large amount of energy, which can have a negative impact on the environment.
- Complexity: Bitcoin and cryptocurrency can be complex and hard to understand for the average person, which can make it difficult for people to use and trust it.
- Illiquidity: Bitcoin market is illiquid, which means that at times it can be hard to find someone to buy or sell the amount you need and at the price you want.
Risks of Investing in BTC
Investing in Bitcoin, like any other investment, carries some risks. Some of the key risks include:
- Volatility: Bitcoin’s value is highly volatile and can fluctuate rapidly in a short period of time. This can make it difficult to predict the value of BTC in the future, and can lead to significant losses if the value drops.
- Lack of regulation: Bitcoin operates in a largely unregulated space, which can increase the risk of fraud and other illegal activities.
- Lack of acceptance: Bitcoin is not yet widely accepted as a form of payment by mainstream merchants and businesses. This can make it difficult to use BTC in everyday transactions.
- Security risks: Bitcoin exchanges and digital wallets have been subject to hacking and theft in the past, which can lead to significant losses for investors.
- Lack of protection: Unlike traditional investments, BTC is not backed by any physical asset or government, and there is no insurance or guarantee of recovery in case of loss.
- Lack of understanding: Bitcoin and cryptocurrency can be complex and hard to understand for the average person, and the lack of understanding can lead to poor investment decisions.
It's important to keep in mind that investing in Bitcoin is considered a high-risk investment and it's not suitable for everyone. It's recommended to do your own research and understand the risks before investing. It's also important to diversify your investments, not to put all your money in Bitcoin or any other single investment.The Bottom Line
Bitcoin has several features that make it different from traditional fiat currencies, such as decentralization, transparency, security, and anonymity. However, it also carries significant risks, such as volatility, lack of regulation, lack of acceptance, security risks and lack of protection.
While Bitcoin is still considered to be a highly speculative investment, many individuals and institutions have begun to invest in it, and it is thought by some to have the potential to become a major player in the global financial system in the future. However, it’s important to note that investing in Bitcoin is high-risk, and it’s important to do your own research and understand the risks before investing. It’s also advisable to diversify your investment portfolio.